First Aid for Insect Stings: Needle and Poison Cases
Reading Time: 15 minutes
Insect stings are a common occurrence, especially during the summer months. Bees, honeybees, wasps, and some other insects may sting humans in defense. While some stings are harmless, others can be poisonous and lead to serious health issues. In this article, we will discuss how to provide first aid for insect stings, when stings may be dangerous, and emergency intervention for poisonous stings.
Dangers Caused by Insect Stings
Insect stings usually result in temporary pain, swelling, and redness. However, in some cases, especially when allergic reactions are involved, insect stings can lead to more severe health issues. Some of the dangerous insect stings include:
- Bee Stings: Bee stings are generally painful but usually heal within a few days. However, for individuals with allergic reactions, there is a risk of anaphylaxis. An allergic reaction involves an exaggerated immune response that can cause low blood pressure, difficulty breathing, and even death.
- Wasp Stings: Wasp stings may be more dangerous when multiple wasps sting at once. Wasps can sting several times. Wasp stings can also trigger allergic reactions.
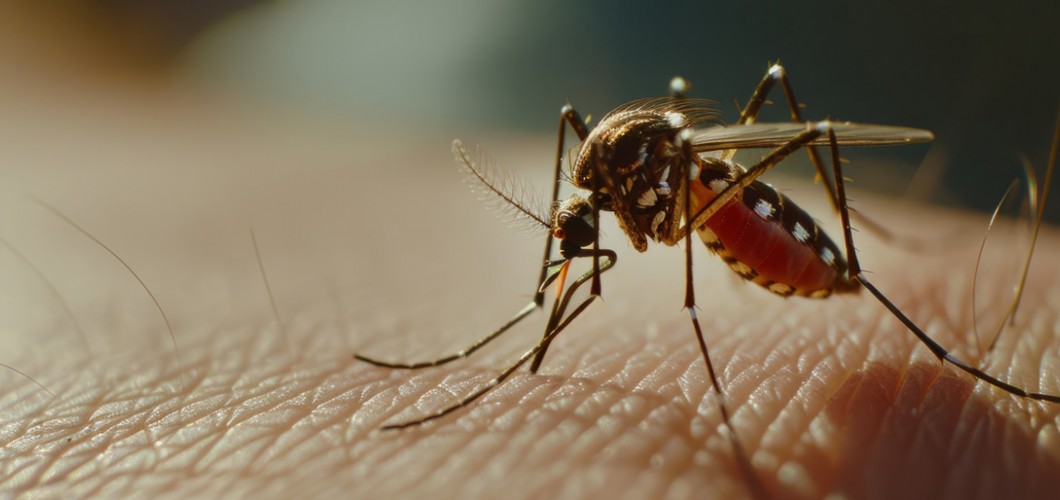
- Mosquito Stings: Mosquito bites usually result in a mild reaction, but certain mosquito species can carry diseases such as Zika virus, malaria, and other illnesses.
Although insect stings typically cause mild swelling, pain, and redness, they can also lead to allergic reactions, infections, or other complications. Therefore, proper intervention is essential.
First Aid Steps for Insect Stings
Insect stings can usually be treated with basic first aid methods. However, the type of sting and the individual's allergic condition must be considered. Here are the basic first aid steps to follow in the event of an insect sting:
1. Stay Calm and Reassure the Victim
Insect stings can cause panic, so the first step is to stay calm. Reassure the person and help them control the situation. Remaining calm is important, as panic can increase the body’s reactions.
2. Clean the Sting Area
The first step is to clean the sting area. Use water and soap to gently clean the area around the sting. Keeping the area clean is important to prevent infection. If the sting is from a bee, carefully remove the bee's stinger from the skin.
3. Apply a Cold Compress to Reduce Swelling and Pain
To reduce swelling and pain after a sting, apply a cold compress. Use an ice pack or a cold cloth for 10-15 minutes on the sting area. This will help reduce swelling and provide relief.
4. Use Antihistamines
If the sting is accompanied by itching, redness, or swelling (signs of an allergic reaction), using an antihistamine may be helpful. Antihistamines help alleviate allergic reactions. However, antihistamines should not be overused, and you should consult a doctor before using them.
5. Avoid Using Heat or Hot Compresses
Applying a hot compress to the sting area can increase swelling and pain. Therefore, avoid using heat on the sting site. Cold compresses are more effective in reducing swelling and relieving pain.
6. Seek Emergency Help for Allergic Reactions
If the person experiences severe itching, difficulty breathing, dizziness, or fainting after the sting, it may indicate an allergic reaction (anaphylaxis). In this case, it is important to call for emergency help and monitor the person's breathing. Allergic reactions can quickly become severe and require immediate medical intervention.
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis from Insect Stings
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction that can occur due to insect stings. This type of reaction typically develops within minutes and spreads rapidly throughout the body. Symptoms of anaphylaxis include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the throat
- Skin rash or hives
- Dizziness or fainting
- Rapid heart rate
- Sudden drop in blood pressure
In cases of anaphylaxis, it is crucial to call for emergency help immediately. An epinephrine injection can improve survival chances, and prompt medical treatment is necessary.
Preventive Measures for Insect Stings
- Wear Protective Clothing: When in areas with high insect activity, wear long-sleeved clothes and pants to reduce the risk of stings.
- Use Insect Repellents: Using insect repellents on the skin can help keep insects away.
- Avoid Contact with Insects: Be cautious in areas where insects are common and avoid disturbing them.
Conclusion
Insect stings typically cause mild discomfort, but they can lead to allergic reactions and other complications that require timely intervention. By following the correct first aid steps based on the type of sting, health issues can be prevented. Always seek professional medical help in cases of allergic reactions and anaphylaxis.

Leave a Comment